Modern style emerged in the late 19th century as a reaction against the eclectic styles that were taking place in Europe. This artistic movement has its maximum expression on decorative arts, but it’s a total style art, wich means it’s also important on painting, sculpture and architecture. It receives many names, the french name ‘Art Nouveau’ is the most known and it’s related to all the contemporary styles that were born in Europe. In Austria, it’s known as ‘Sezession’, in Spain, ‘Modernismo’, in Germany, ‘Jugendstil’, and elsewhere it’s known by other names, but it always have similar characteristics.
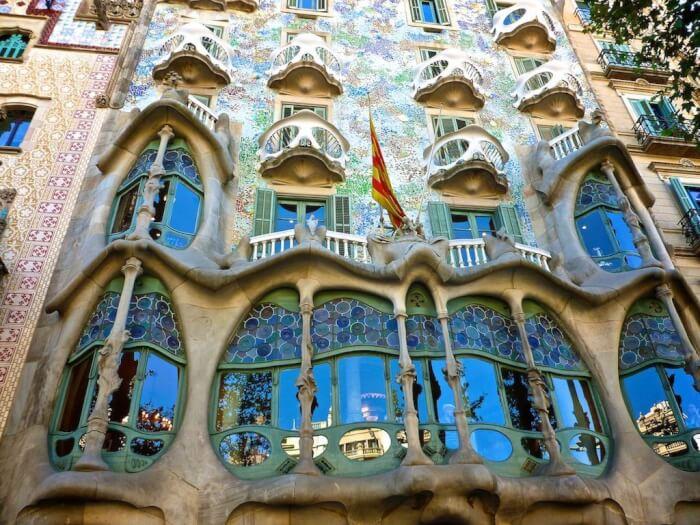

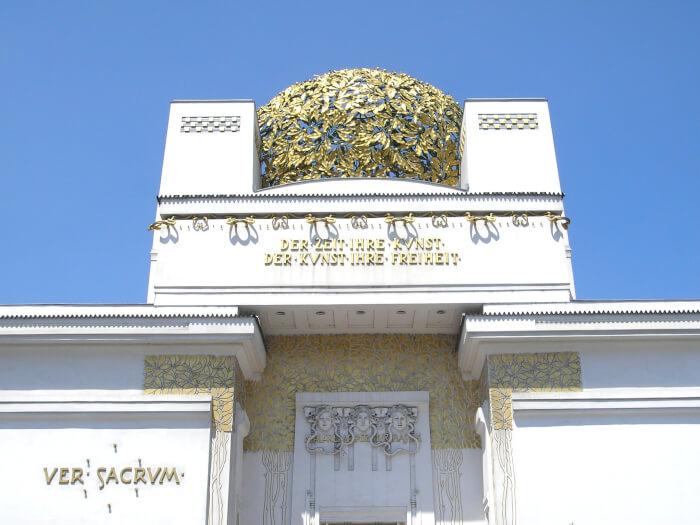
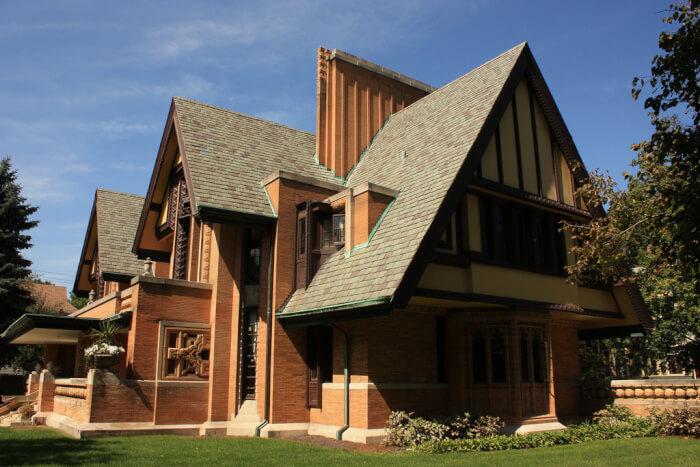
The main feature is the desire to break with the previous styles. The pre-origins are in Britain, inspired in the floral designs of William Morris, and the Arts and Crafts movement developed there. The style is quite different in France, where there is a mixture of trends. In architecture, can be seen the influence of the historian and architectural theorist Eugène Viollet-le-Duc, known detractor of Beaux-Arts style, in whose book ‘Entretiens sur l’architecture’ were inspired architects like Hector Guimard, Louis Sullivan, or Antoni Gaudí. The real beginning of the modern architecture is in Belgium with Victor Horta, known for the Hotel Tassel, or Henry van de Velde, author of his residential house, Bloemenwerf.
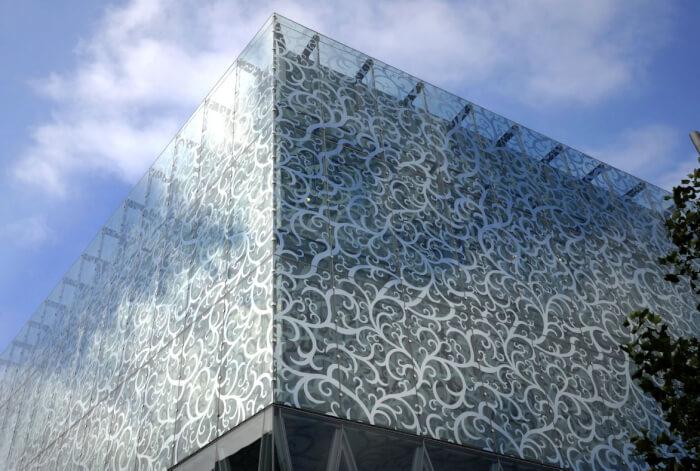
There are common details in modern buildings from all Europe. The inspiration in nature and the use of natural elements, and vegetation for the ornaments, are very frequent. Depending on the main tendency of the country, it uses the straight line and the geometry, like Olbrich or Wagner, or the curved line and asymmetry, like Guimard or Gaudí whose forms are soft and rounded. The stylization of the motives, far from its realistic representation, gives elegance to this style. The movement takes advantage of the industrial revolution resources, and uses glass and iron to contribute to the architecture of the buildings, not only for the facade and decoration, but also windows, stairs, grilles and more.